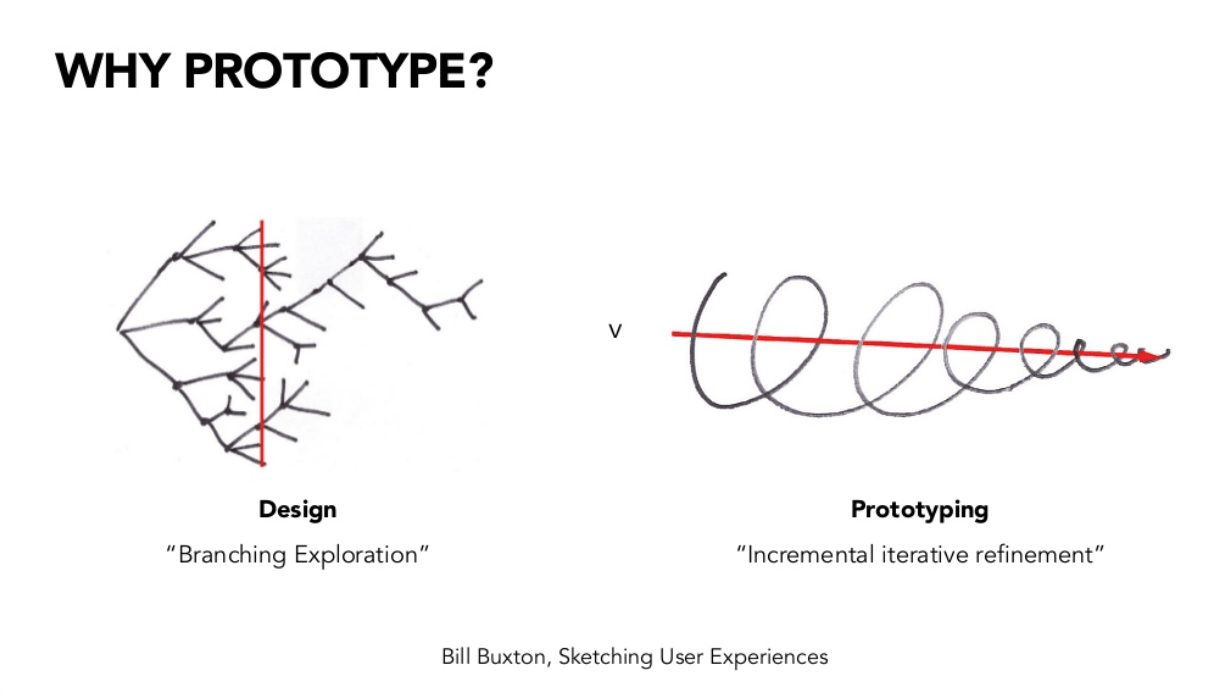
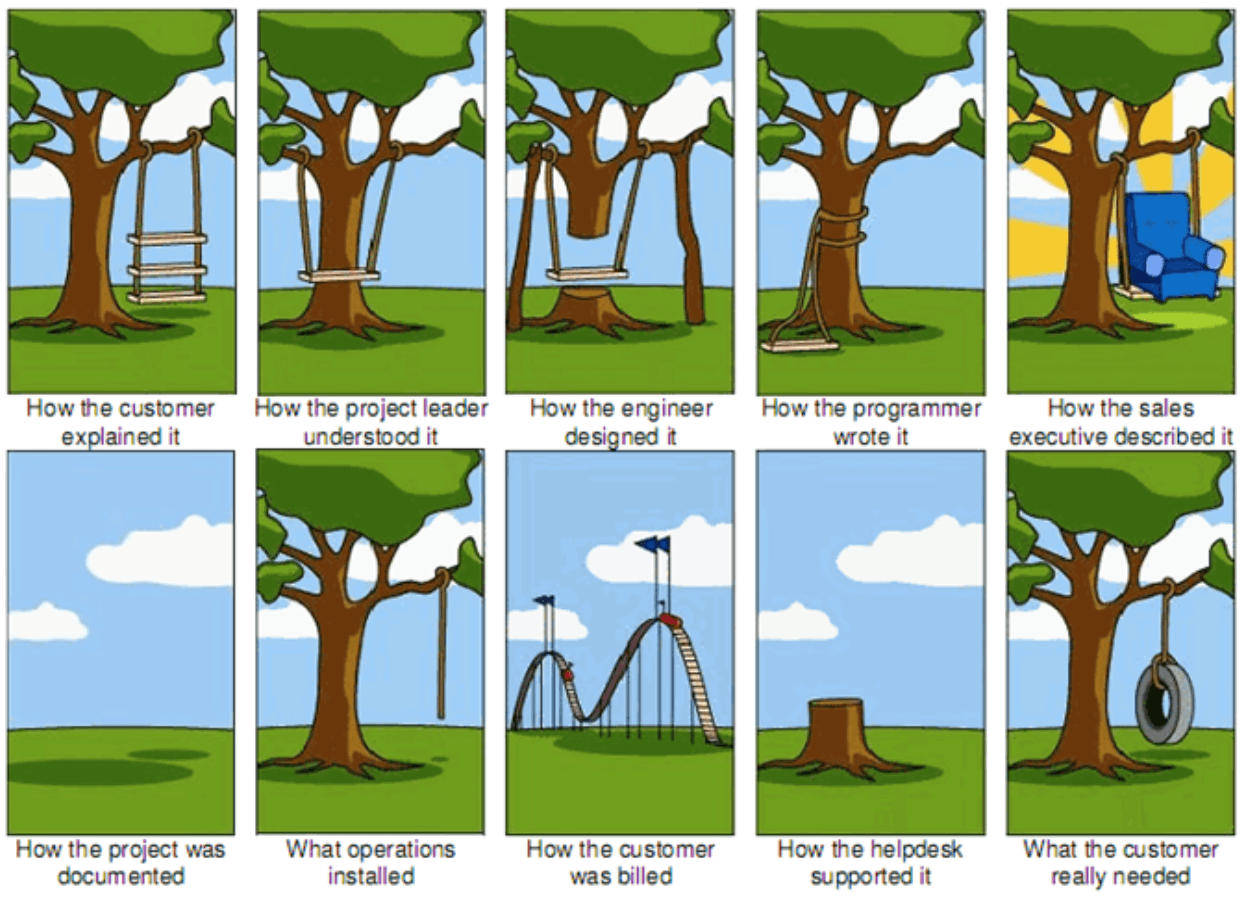
Explain the features of the design supply chain
The Design Chain consists of four major stages
- Discover: Market research, User research, Managing information and Design research groups. This stage is the start of the design chain. This begins with an initial ideas or inspiration. This is the stage where needs are identified.
- Define: This is the second phase of the design chain where needs are identified, whether it be client needs or business needs. This will involve Project development, Project Management and Project sign-off
- Develop: This is the third stage of the design chain which includes the design led solutions into development, here designs are prototyped and tested against original specifications of the design brief. This includes Multi-disciplinary working, visual management, development methods and Testing
- Deliver: The final stage is where the design is finalized and launched into the relevant market place. The key activities for this stage includes final testing, approval and launch, Targets, evaluation and feedback loops
| Explain how different business contexts may impact on the design process There could be a range of different contexts that would impact on the design process and they include the following
Outline how to relate the design process to different business needs
|
This is the first phase of the design process where we identify market trends, and client needs.
This will be developed through market research, user research, managing information, design research groups.
Research could be obtained through surveys, social media, website enquirers, latest
fashion trends.
This is the Define stage of the design process
Outline the key features of the design process
Design Brief: is a document which outlines the requirements of the design
Research: This is where we research the design brief
Initial ideas: conceptualising, sketching, experimenting, possible material ideas
Reflection and feedback, client, design manager, surveys
Revisions: Which designs will be suitable, this may involve cost, time, materials. client feedback, Design manager feedback.
Prototype: experiment with a design idea whether it be a 2D presentation or 3D modelling.
A prototype is an example of what the final design will look like
Presentation if final design idea which is show cased to the client 2D hard copy for example print design, 3D sample in the relevant materials.
Delivery of the final idea for realisation, final sign off stage by the client or stake holder.
Feedback back...client, design manager, surveys, research groups, sample market, social media.
Explain how creative thinking techniques can be used to generate ideas in any design context
Creative thinking techniques could include the following areas
- Brainstorming
- Focus Groups
- Analysis of existing designs
- Conceptualising
- Defining
- Examining
- Listening, market research feedback
- Questioning
- Synthesis
- Evaluating information
These processes can help to generate design ideas...see blooms taxonomy diagram.
Here are examples of the creative thinking techniques that can be used to help generate creative ideas.
De Bono's six thinking hats to help develop new ideas
De Bono's six thinking hats to help develop new ideas
Describe the purpose of using prototypes, proofs and mock-ups in the design process Nothing brings you closer to the functionality of the final product than prototyping. While sketching out the final idea and mock ups show the feel and texture of the design, it is the prototype that brings to life the “experience” behind “user experience.” Here is an example of a life size model of a BMW created in clay |
Describe potential sources of information for new ideas, relevant to a specific design process.
Here are a range of secondary and primary resources to help with design ideas
- Art Galleries: Primary resource looking at current designers and products
- Internet: showing latest trends in design, update resource
- blogs updated daily on information relating to design.
- Magazines: Specific to design and designers latest work and current trends, eg technology
- Library: Secondary resource where a central resource for a range of design issues
- Your Environment: Secondary resource looking at whats around us, for example latest graphical poster trends in advertising
- Media, games, films, TV: Secondary resource looking at latest technological developments in Design.
- Fashion and shopping: Design trend sin style, colour and fabrics.
- Museums
- Books
- Studios and workshops
- Tutor
- Each other
- Sporting events
- Holidays
- Music Events
- Trends
- Posters and print design
- Cultural Influences
Explain how copyright, moral rights, and intellectual property rights may impact on the design process
Copyright:is a legal right created by the law of a country that grants the creator of an original work exclusive rights for its use and distribution. This is usually only for a limited time. The exclusive rights are not absolute but limited by limitations and exceptions to copyright law, including fair use. A major limitation on copyright is that copyright protects only the original expression of ideas, and not the underlying ideas themselves
Copyright protection for the lifetime of the creator plus 70 years

Moral Rights
Human beings have fundamental rights that cannot be taken away by another individuals decision
- Privacy
- Freedom of speech
- Culture
- Religion and belief
- Sexuality
- Equality and Diversity
- Race
- Age
- Disability
- Gender reassignment
- Marriage and civil partnerships
- Pregnancy and maternity
- Gender
- Sexual orientation
Intellectual Property rights
Having the right type of intellectual property protection helps you to stop people stealing or copying:
- the names of your products or brands
- your inventions
- the design or look of your products
- things you write, make or produce
Copyright, patents, designs and trade marks are all types of intellectual property protection.